
Did you know that the global electric scooter market is expected to reach $41.98 billion by 2030?
That’s a lot of e-scooters – and plenty of batteries! As a fervent e-rider, you might be wondering what happens to all those lithium-ion powerhouses when they’ve zipped their last mile. Well, buckle up (or should I say, charge up?) because we’re about to dive into the electrifying world of recycling electric scooter batteries!
The Anatomy of Electric Scooter Batteries
Electric scooter batteries are marvels of modern engineering, providing substantial power in a compact size. Understanding their composition is important for appreciating the complexities and significance of recycling electric scooter batteries. Let’s break down these power cells and explore the technology that keeps you zipping through the town.
Lithium-Ion Technology: The Heart of E-Scooter Power
At the core of every electric scooter is a lithium-ion battery, the unheralded champion of the e-mobility revolution. These batteries consist of four key components: the cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator.
The cathode and anode store and release lithium ions, while the electrolyte facilitates their movement. The separator keeps the cathode and anode apart, thus helping prevent short circuits.
Lithium-ion batteries are the consumer choice for e-scooters due to their high energy density and durability. Common chemistries include LiNiMnCoO2 (NMC) and LiFePO4 (LFP), each offering unique advantages. NMC batteries provide higher energy density, while LFP batteries offer better thermal stability and longer lifespans.
The composition of these batteries directly impacts their recycling potential. For instance, NMC batteries contain valuable metals like cobalt and nickel, making them appealing for recycling. However, the intricate blend of materials might hinder the recycling process.
Battery Management Systems (BMS): The Unsung Heroes
While the battery cells do most of the work, the Battery Management System (BMS) is the brain behind the operation.
The BMS monitors and manages the battery’s performance, ensuring optimal operation and longevity. It regulates charging and discharging, balances cell voltages, and prevents overheating or overcharging.
Hence, this improves the user experience, while delaying the need for recycling electric scooter batteries. Moreover, when it is time for recycling, the data stored in the BMS can provide valuable insights into the battery’s health and usage history, potentially optimizing the recycling process.
The Environmental Impact of E-Scooter Batteries
As we embrace the eco-friendly promise of electric scooters, it’s crucial to consider the full lifecycle of their batteries. While e-scooters offer a greener alternative to traditional vehicles, the production and disposal of their batteries come with their own ecological issues. Let’s explore these, along with the role of recycling in rectifying their impact.
The Good, the Bad, and the Lithium
Electric scooters have been projected as a green transportation solution, but the reality is more complex. The production of lithium-ion batteries does have a significant carbon footprint. However, ecologically, as compared to the lifetime emissions of traditional vehicles, e-scooters still outshine them.
| Vehicle Type | Production Emissions (kg CO2e) | Lifetime Emissions (kg CO2e/km) |
| E-Scooter | 50-150 | 0.02-0.05 |
| Car (petrol) | 5,500-7,000 | 0.15-0.25 |
| Bicycle | 30-100 | 0.005-0.015 |
Recycling electric scooter batteries becomes crucial when e-scooter batteries are improperly disposed of. As lithium-ion batteries end up in landfills, they can leak toxic materials into the soil and water.
The concept of “urban mining” is gaining popularity in the world of battery recycling. This refers to the practice of recovering valuable materials from discarded electronics, including e-scooter batteries. By recycling these batteries, we can reduce the need for new raw material extraction, significantly lowering the overall environmental impact.
Rare Earth Elements: The Hidden Treasure in Your Battery
E-scooter batteries contain more than just lithium. They’re a treasure trove of rare earth elements, including cobalt, nickel, and manganese. While these are necessary for battery performance, they also pose certain environmental threats.
Fact Box: Rare Earth Elements in E-Scooter Batteries:
- Cobalt: Essential for battery stability, but mining practices are often unethical
- Nickel: Improves energy density, but mining can cause severe environmental damage
- Manganese: Enhances battery life, with relatively lower environmental impact
- Lithium: The key ingredient, but extraction can deplete water resources
The global demand for these elements is skyrocketing, pressurizing limited resources. Recycling electric scooter batteries can help alleviate this demand by replenishing these valuable materials. Some innovative battery technologies are further researching on ways to reduce reliance on rare earth elements, potentially making future e-scooter batteries even more sustainable.
The Lifecycle of an E-Scooter Battery
Studying the journey of an e-scooter battery from its production to recycling can highlight the importance of proper disposal and recycling. This lifecycle consists of several stages, each with its own impact on the battery’s performance and environmental footprint.
From Factory to First Ride
The life of an e-scooter battery begins in a high-tech factory, where raw materials are transformed into useful energy storage devices. The manufacturing process involves diligently assembling the cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator into a compact package. Quality control at this stage is crucial, as it directly affects the battery’s lifespan and recyclability.
Proper care of the battery starts even before its first ride. Many manufacturers are now implementing “battery passports” – digital records that track a battery’s journey from production to recycling. These passports may incorporate information about the battery’s composition, performance, and usage history, potentially streamlining the recycling process at the end of its life (similar to the function of BMS).
| Practice | Impact on Lifespan | Impact on Recyclability |
| Regular charging | Positive | Neutral |
| Avoiding extreme temperatures | Positive | Positive |
| Proper storage when not in use | Positive | Positive |
| Overcharging | Negative | Negative |
| Physical damage | Negative | Negative |
Signs Your Battery is Ready for Retirement
Even with the best care, all batteries eventually reach the end of their life. Recognizing the signs of battery degradation is necessary for maintaining the performance and safety of your e-scooter. Some common indicators may be:-

Most e-scooter batteries have an average lifespan of 2-3 years or 300-500 charge cycles.
However, this can vary based on usage patterns, environmental conditions, and battery quality. When your battery shows signs of significant degradation, it’s time to consider recycling electric scooter batteries.
Before recycling, some batteries might be suitable for “second life” applications. These are less demanding uses where the battery’s reduced capacity isn’t a significant issue. For example, a battery that can no longer power an e-scooter might still be useful for energy storage in less strenuous scenarios.
The Recycling Process: From Scrap to Reborn
Recycling electric scooter batteries is a complex process that involves several stages, from collection to material recovery. Let’s break down the journey of an e-scooter battery from end-of-life to rebirth in order to fully recognize the significance of its proper disposal and effects on the environment.
Collection and Sorting: The First Steps
The recycling process begins with the collection of retired batteries. This stage presents unique challenges due to the distributed nature of e-scooter usage. Many cities and e-scooter companies are implementing battery take-back programs to facilitate collection. Some innovative approaches include automated battery drop-off points in urban areas.
Once collected, batteries need to be sorted based on their chemistry and condition. Proper labeling and identification are essential at this stage. Batteries with different chemistries (like NMC and LFP) require differing recycling processes. Some recycling facilities use advanced sorting technologies, such as X-ray fluorescence, to identify battery types accurately.
Breaking It Down: The Recycling Technologies
Q: How does pyrometallurgical recycling work?
A: This method involves heating the batteries to high temperatures, melting the metals for recovery. It’s effective but energy-consuming.
Q: What about hydrometallurgical recycling?
A: This process uses chemical treatments to extract metals. It’s more precise and can recover a wider range of materials.
Q: Are there any new recycling technologies on the horizon?
A: Yes, direct recycling is an emerging method that aims to recover cathode materials in a form that can be directly reused in new batteries.
Q: What is “black mass” in battery recycling?
A: Black mass is the mixture of valuable metals (like cobalt, nickel, and lithium) left after the initial crushing and separation of battery components.
Q: How efficient are these recycling methods?
A: Efficiency varies, but advanced processes can recover up to 95% of the battery’s valuable materials.
The Future of Recycling E-Scooter Batteries
As the e-scooter industry continues to grow, so does the need for efficient and sustainable battery recycling solutions. The future of recycling electric scooter batteries is bright, with innovations in technology and policy paving the way for a more circular e-mobility ecosystem. Let’s explore what the future might hold for e-scooter battery recycling and how it could impact the industry.
Innovations on the Horizon
The world of battery recycling is buzzing with advancements. One exciting area of development is biological recycling, which uses bacteria to extract metals from batteries. This method could potentially be more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional recycling methods.
Another important trend is the concept of “design for recycling.” Battery manufacturers are increasingly considering the end-of-life stage during the design process, making batteries easier to disassemble and recycle. This could significantly optimize recycling and reduce costs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also being incorporated into battery recycling. These technologies can streamline sorting processes, predict battery life more accurately, and even improve the efficiency of recycling plants. As these technologies evolve, we can expect to see more automated and efficient recycling processes.
The ultimate goal for many in the industry is to achieve closed-loop recycling for e-scooter batteries. This would mean that materials recovered from old batteries could be directly used to manufacture new ones, creating a truly circular economy for e-mobility.
Policy and Regulations: Shaping the Recycling Landscape
The future of recycling electric scooter batteries isn’t just about technology – policy and regulations have an equally important impact. Many governments are introducing or strengthening regulations around battery recycling. The concept of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is gaining traction, making manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling.
In the European Union, for example, proposed regulations aim to make batteries more sustainable throughout their lifecycle. These could set new standards for battery design, durability, carbon footprint, and recycled content. Similar initiatives are being considered in other parts of the world.
Government incentives are also likely to play a bigger role in promoting battery recycling. These could include tax breaks for companies investing in recycling technologies or subsidies for consumers who choose to properly dispose of their e-scooter batteries.
Standardization efforts are also worth paying attention to. As the e-scooter industry develops further, we might see more standardized battery designs. This could greatly simplify, and thus streamline the recycling process, as recycling facilities wouldn’t need to deal with as many different battery types and chemistries.
What Can You Do? The E-Rider’s Role in Battery Recycling
As an e-scooter enthusiast, your riding habits, maintenance practices, and disposal choices can significantly impact the battery durability and its recyclability. Here’s how you can contribute to the sustainable future of e-mobility through responsible battery use and recycling.
Proper Care and Maintenance: Extending Battery Life
Taking good care of your e-scooter battery not only enhances your riding experience but also delays the need for recycling electric scooter batteries. Some tips to keep your battery in good shape include:-
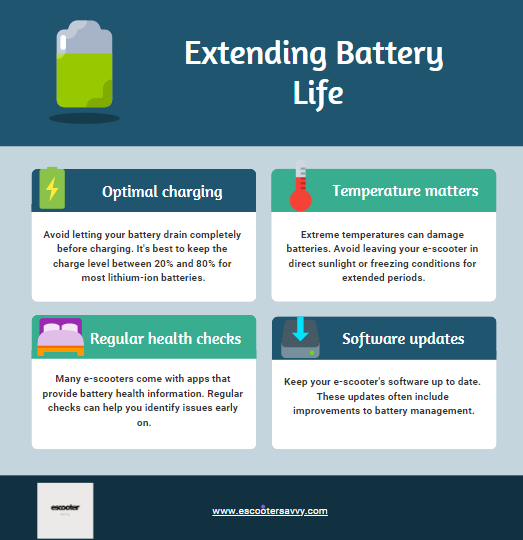
Furthermore, understanding how to interpret battery health data can help you make informed decisions about when to consider recycling. Most e-scooter apps provide information on battery capacity and charge cycles. If you notice a significant drop in capacity (usually below 80% of original), it might be time to consider recycling options.
End-of-Life Options: Making the Right Choice
When your e-scooter battery nears the end of its life, it’s crucial to dispose of it responsibly. Here’s what you should know about recycling electric scooter batteries:
- Safe removal: If you need to remove the battery yourself, follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Lithium-ion batteries can be dangerous if handled improperly.
- Recycling options: Many e-scooter manufacturers offer take-back programs for their batteries. Alternatively, look for certified electronics recycling centers in your area.
- Verify recycling claims: Not all recycling facilities are created equal. Do some research to ensure that the facility you choose actually recycles the batteries rather than just storing them.
- Consider refurbishment: In some cases, batteries that no longer meet e-scooter standards might be refurbished for less rigorous applications. This can extend the battery’s useful life before recycling.
Conclusion:
As we’ve zipped through the intricate world of e-scooter battery recycling, it’s obvious that our role as e-riders goes well beyond just the last ride. By understanding the lifecycle of our batteries and making thoughtful decisions about their disposal, we’re not just powering our commutes – we’re energizing a more sustainable future for urban mobility.
Recycling electric scooter batteries is more than just a responsible choice – it’s a crucial step in developing a circular economy for e-mobility. From the rare earth elements that power our rides to the innovative technologies that give these batteries a second life, every aspect of the recycling process contributes to a greener future.
So, the next time you hop on your e-scooter, remember: you’re not just riding on two wheels, you’re riding on an e-mobility revolution. Let’s keep that revolution rolling, one responsibly recycled battery at a time!
Comments
[…] the essential features of electric scooters tailored for hunting, focusing on their power, battery life, and terrain management capabilities. Each feature is designed to enhance performance, reliability, […]